MariaDB As Backend With Node.js And Express.js
Here’s how to build a robust API. You can do it.
This is the backend of MariaDB.
What is MariaDB?
MariaDB is a rational database and a fork of MySQL. It has a similar syntax to MySQL.
It was released in 2009.
The base
AlmaLinux 9.7
DNF version: 4.14
The setup
Setup the database in MariaDB
MariaDB Database Setup
Before starting the API server, ensure your database and table are set up. Connect to MariaDB and run the following SQL commands (adjusting data types as necessary):
SQL
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS Postsendungen;
USE Postsendungen;
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS Briefe (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
Firma VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
Strasse VARCHAR(255),
PLZ VARCHAR(10),
Stadt VARCHAR(255),
Datum DATE,
Ansprechpartner VARCHAR(255),
Betreff TEXT
);
-- Optional: Insert some test data
INSERT INTO Briefe (Firma, Datum, Betreff) VALUES ('Example Corp', NOW(), 'Initial Test Letter');Installation of Node.Js
AlmaLinux installs the version 1:16.20.2-8 but in order to run Express.js you should have Node.JS 20.
You go to the terminal and type in:
sudo dnf module list nodejs
Name Stream Profiles Summary
nodejs 18 common [d], development, minimal, s2i Javascript runtime
nodejs 20 common [d], development, minimal, s2i Javascript runtime
nodejs 22 common [d], development, minimal, s2i Javascript runtime
nodejs 24 common [d], development, minimal, s2i Javascript runtime
Hinweis: [d]Standard, aktivi[e]rt, [x]deaktiviert, [i]nstalliert
I decided to take version 20. The next command is:
sudo dnf module reset nodejs
Installation of Node.js version 20
[skramer@linux mariadb_api]$ sudo dnf module enable nodejs:20
Then you have to install it.
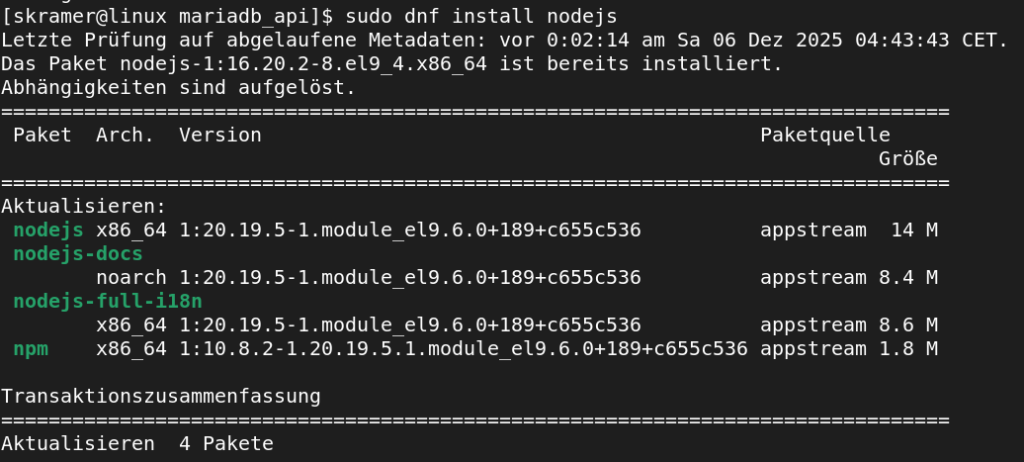
You see, I have now the version 1:20.19.5.1 instead of 1:16.20.2-8.
After that you install via npm MariaDB and Express
npm install mariadb express cors
Creating the folder
mkdir maria_api
and the move into this folder
cd maria_api
The next step is to create the server.js
My server.js
// server.js (MariaDB + Express.js API)
// **********************************************
// 1. MODULE IMPORTIEREN
// **********************************************
const express = require('express');
const mariadb = require('mariadb');
const cors = require('cors'); // important for the frontend
// **********************************************
// 2. KONFIGURATION
// **********************************************
const app = express();
const PORT = 3000;
// MariaDB Verbindungspool
const pool = mariadb.createPool({
host: 'localhost',
port: 3306,
database: 'Postsendungen', // 🛑 important to take a real database name
user: 'sven',
password: 'PW', // to take a real password
connectionLimit: 5,
// WICHTIGE ERGÄNZUNG:
// Weist den Treiber an, BIGINT als Zeichenketten zu behandeln,
// da JSON den Typ BigInt nicht unterstützt.
supportBigNumbers: true,
bigNumberStrings: true
});
// **********************************************
// 3. MIDDLEWARE & DATENBANK-SETUP
// **********************************************
app.use(cors()); // permits the access to the index.html
app.use(express.json()); // Erlaubt das Verarbeiten von JSON-Daten im Request Body
// Init-Check der Datenbankverbindung
pool.getConnection()
.then(conn => {
console.log('✅ MariaDB Pool Verbindung erfolgreich hergestellt.');
conn.release();
})
.catch(err => {
console.error('❌ MariaDB Verbindung fehlgeschlagen:', err);
});
// **********************************************
// 4. EXPRESS ROUTING (API-ENDPUNKTE)
// **********************************************
// --- 4a. Basis Test-Endpunkt ---
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send(`<h1>Express API läuft!</h1> Verbunden mit MariaDB an Port ${PORT}.`);
});
// --- 4b. API-Endpunkt zum Abrufen aller Benutzer (Beispiel: SELECT) ---
// ANNAHME: Sie haben eine Tabelle 'users' in Ihrer DB
app.get('/api/briefe', async (req, res) => {
let conn;
try {
conn = await pool.getConnection();
// Führt die SQL-Abfrage aus
const rows = await conn.query("SELECT id, Firma, Strasse, PLZ, Stadt, Datum, Ansprechpartner, Betreff FROM Briefe");
res.json({
anzahl: rows.length,
ergebnisse: rows
});
} catch (error) {
console.error("MariaDB Abfragefehler:", error);
res.status(500).json({ message: 'Fehler beim Abrufen der Benutzerdaten.', error: error.message });
} finally {
if (conn) conn.release(); // Verbindung freigeben ist obligatorisch!
}
});
// **********************************************
// 5. SERVER STARTEN
// **********************************************
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log(`🚀 Server gestartet auf http://localhost:${PORT}`);
});To create the index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="de">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>MariaDB API Test</title>
<style>
body { font-family: sans-serif; max-width: 800px; margin: 0 auto; padding: 20px; }
h1 { color: #007bff; }
button { padding: 10px 15px; background-color: #28a745; color: white; border: none; cursor: pointer; margin-bottom: 20px; }
#ergebnisse { margin-top: 20px; border: 1px solid #ccc; padding: 15px; white-space: pre-wrap; background-color: #f8f8f8; font-family: monospace; }
.success { color: green; font-weight: bold; }
.error { color: red; font-weight: bold; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
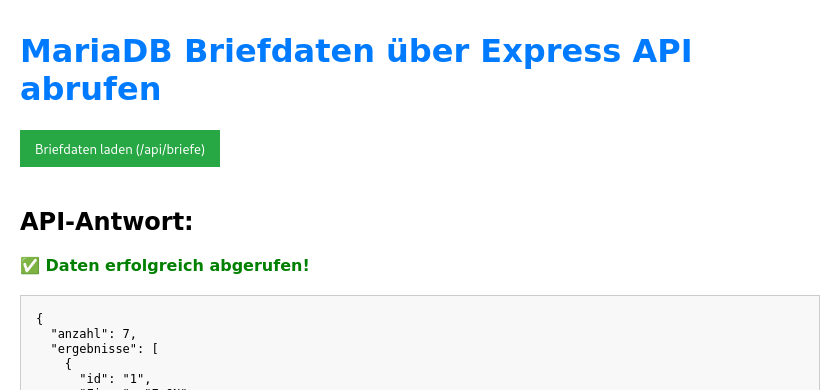
<h1>MariaDB Briefdaten über Express API abrufen</h1> <button onclick="fetchUserData()">Briefdaten laden (/api/briefe)</button> <h2>API-Antwort:</h2>
<div id="statusMeldung">Klicken Sie auf den Button, um die Daten zu laden.</div>
<div id="ergebnisse"></div>
<script>
async function fetchUserData() {
const statusDiv = document.getElementById('statusMeldung');
const ergebnisDiv = document.getElementById('ergebnisse');
// URL hier ANPASSEN
statusDiv.textContent = 'Lade Daten von http://localhost:3000/api/briefe...';
ergebnisDiv.textContent = '';
try {
// Führt die GET-Anfrage an den Express-Endpunkt aus
const response = await fetch('http://localhost:3000/api/briefe'); // ANGEPASST
const daten = await response.json();
if (response.ok) {
statusDiv.innerHTML = '<span class="success">✅ Daten erfolgreich abgerufen!</span>';
ergebnisDiv.textContent = JSON.stringify(daten, null, 2);
} else {
statusDiv.innerHTML = `<span class="error">❌ Fehler (${response.status}):</span> ${daten.message || 'Unbekannter Fehler'}`;
ergebnisDiv.textContent = JSON.stringify(daten, null, 2);
}
} catch (error) {
statusDiv.innerHTML = `<span class="error">❌ Netzwerkfehler:</span> ${error.message}. Läuft der Server (node server.js)?`;
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>In the command line, I started then
node server.js and
In the web browser
CTRL + F the index.html.