Linux: What is a repo file?
A repo file is a text file that contains instructions for the operating system (Linux, the Bash) where to find the newest information about a package.
In contrast to operating systems like Microsoft Windows, where you download and install software directly from a variety of sources, Linux distributions rely on these central repositories. This structure allows the distribution maintainers to check and verify the packages for stability and security before they reach your system.
🚩️ Warning: While you can install software manually without using a package manager and its repos (e.g., by compiling from source or using a direct
.rpm/.debfile), you do so at your own risk. If dependencies conflict or a security issue arises, it is entirely your problem to solve. 🚩️
You can open the repo file with every text editor and the cat command in Linux.
The file contains the URL to the server, a check about GPG = GNU Privacy Guard – a cryptographic software that was introduced in 1999.
The repos are stored in the direction in Red-Hat Family (like Fedora, AlmaLinux, Rocky Linux) distribution:
/etc/yum.repos.d
In Debian (like Ubuntu and Linux Mint) distributions:
/etc/apt/sources.list
Here is a small repo from the repo of MongoDB
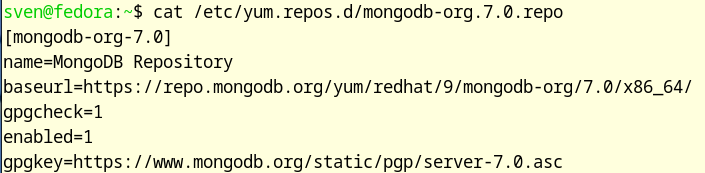
First, you see the current version.
[Section Name]A unique ID for the repository (e.g.,mongodb-org-7.0).nameA human-readable description of the repository.baseurlThe URL of the server where the package manager looks for files.gpgcheckGPG (GNU Privacy Guard) Check. A cryptographic measure to verify the integrity and origin of the packages.1means enabled,0means disabled.enabledStatus.1means the repository is actively included as a package source,0means it is ignored.gpgkeyThe file location (URL or local path) of the public GPG key used for verification.
Where you find the exact values?
Go to the software manufacture website in most cases there is an installation point and there the software manufacture has published the exact information what kind of information you need for this repo.
You can use every text editor what you like (VIM, gedit, Mousepad, nano, joe etc..). The important thing, is that the extension of the text file is .repo.
Go to the installation instruction of the software manufacture, because you have to enable this file into the system.
What is the advantage and disadvantage of a repo?
Only external software like MongoDB, MySQL and Visual Studio Code have this information. With the repo, you have the guarantee that you get the newest updates. In most cases, these are security updates. It is not so very common that you get a new function in your software.
What is the easiest way to get the repo list?
dnf repolist
code Visual Studio Code
fedora Fedora 41 – x86_64
fedora-cisco-openh264 Fedora 41 openh264 (From Cisco) – x86_64
mongodb-org-7.0 MongoDB Repository
mysql-8.4-lts-community MySQL 8.4 LTS Community Server
mysql-connectors-community MySQL Connectors Community
mysql-tools-8.4-lts-community MySQL Tools 8.4 LTS Community
rpmfusion-free RPM Fusion for Fedora 41 – Free
rpmfusion-free-updates RPM Fusion for Fedora 41 – Free – Updates
rpmfusion-nonfree RPM Fusion for Fedora 41 – Nonfree
rpmfusion-nonfree-updates RPM Fusion for Fedora 41 – Nonfree – Updates
updates Fedora 41 – x86_64 – Updates
Which commands uses the repolist?
- dnf upgrade -y –refresh
- dnf info
- dnf search
- dnf check-update
Others
It is advisable to do a backup of your repos. Yes, the distribution main repos in my case Fedora and AlmaLinux come with the installation process, but your special repos in my case from MongoDB or Visual Studio Code you should save it in a ZIP file. In most cases you don’t need it not, but in a case of a malfunction then you have the original repo list again, and you don’t need to search it on the internet.
„OpenSource Traveler,“ founded on October 6, 2025. I am self-employed and offer Linux courses covering these types of topics.